Many contraceptive pills contain the same active ingredients but can still affect individuals differently. Rigevidon and Microgynon are two commonly prescribed combined contraceptive pills that work in similar ways to prevent pregnancy. However, users often report differences in how they experience side effects, tolerance, and availability.
If you’re trying to decide between Rigevidon and Microgynon, understanding their similarities and differences is key. While both pills contain the same hormones, small variations in their formulations may influence how they suit different people. Factors such as side effects, personal health history, and previous contraceptive experiences can all play a role in determining which option is best for you.
This article will compare Rigevidon and Microgynon to help you make an informed choice about your contraceptive needs.
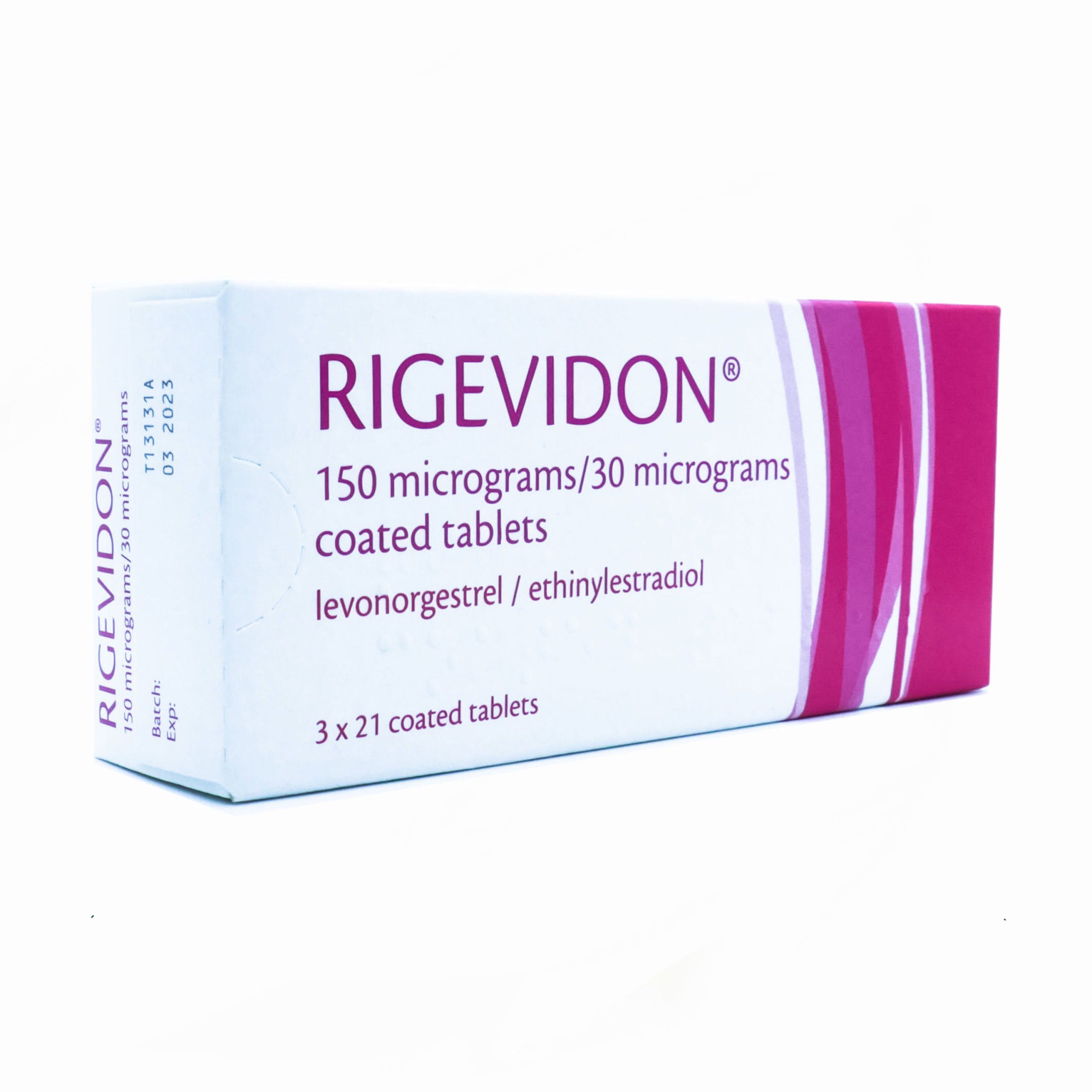
What Is Rigevidon?
Rigevidon is a combined oral contraceptive pill that contains ethinylestradiol (30 micrograms) and levonorgestrel (150 micrograms). These two hormones work together to prevent pregnancy in three ways:
- Stopping ovulation – preventing the release of an egg from the ovaries.
- Thickening cervical mucus – making it harder for sperm to reach the egg.
- Thinning the uterine lining – reducing the likelihood of implantation.
Rigevidon is a widely used contraceptive pill, often prescribed as a cost-effective, generic alternative to branded pills like Microgynon. Despite having the same active ingredients, some users report differences in how they experience side effects when switching between brands.
This pill follows a 21-day cycle, meaning you take one Rigevidon tablet daily for 21 days, followed by a 7-day break during which a withdrawal bleed occurs. It is available on prescription and is one of the most commonly dispensed combined contraceptive pills in the UK.
What Is Microgynon?
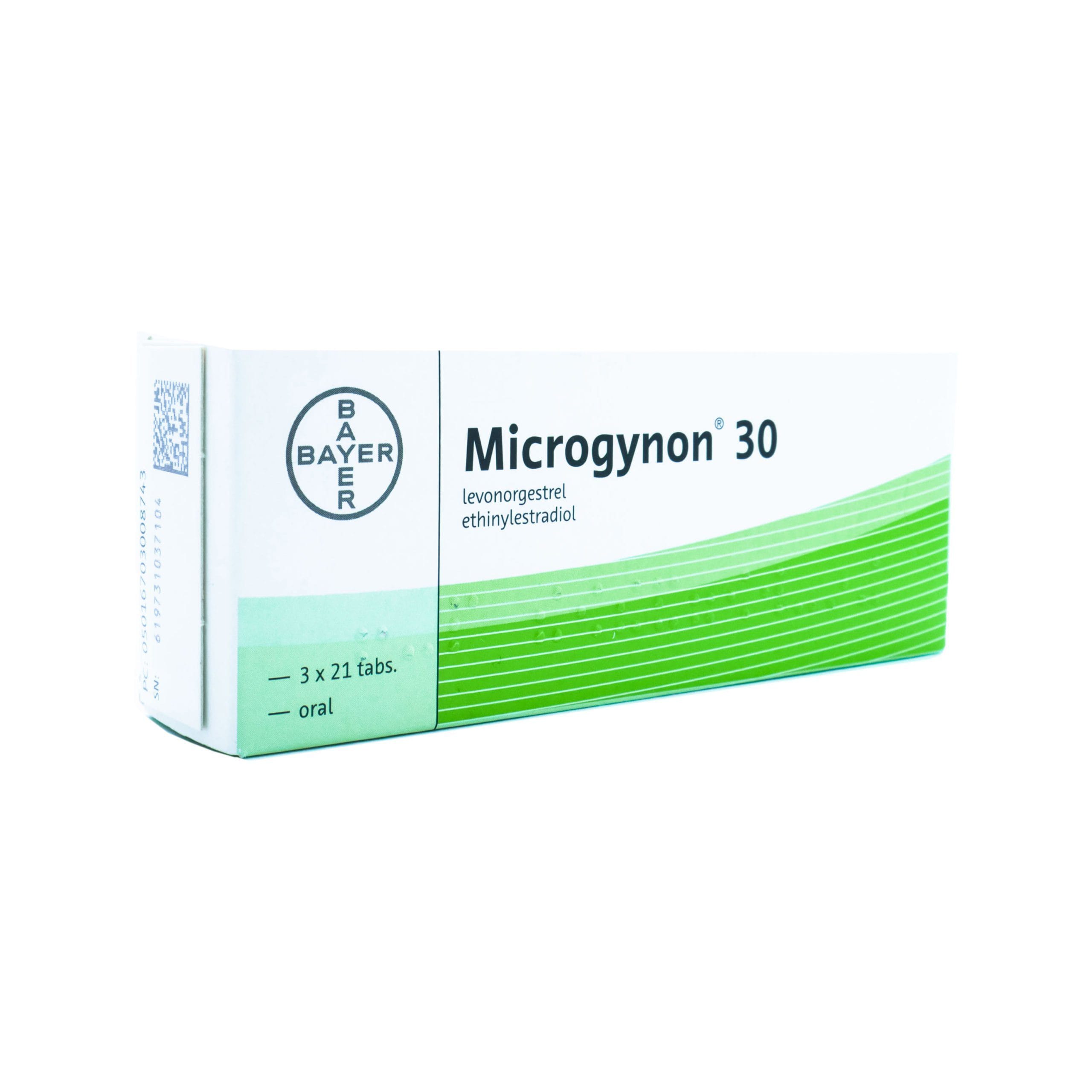
Microgynon is another combined oral contraceptive pill that contains the same active ingredients as Rigevidon (ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel). It works in the same way to prevent pregnancy by stopping ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and thinning the uterine lining.
As one of the longest-standing and most widely prescribed contraceptive pills, Microgynon has built a reputation for reliability and effectiveness. Many healthcare providers prescribe it as a first-choice contraceptive pill due to its well-established safety profile and availability.
Like Rigevidon, Microgynon is typically taken in a 21-day cycle, followed by a 7-day break. Some pharmacies and healthcare providers may offer Microgynon as a branded version, which can result in differences in packaging, cost, and inactive ingredients compared to generic alternatives. However, its hormonal composition remains the same.
Key Differences Between Rigevidon and Microgynon
Although Rigevidon and Microgynon contain the same active ingredients, some users report differences due to inactive ingredients and branding.
- Branding & Packaging – Microgynon is a branded pill, while Rigevidon is a generic alternative often prescribed for cost-effectiveness.
- Inactive Ingredients – Differences in fillers and coatings may affect tolerance, even though the active hormones are identical.
- User Experience – Some users find one pill causes fewer side effects than the other, possibly due to formulation differences.
- Availability & Cost – Microgynon may be more widely stocked, but Rigevidon is often the cheaper option.
While these pills work the same way, individual reactions can differ. If switching between them leads to unexpected side effects, consult a doctor to discuss alternatives.
Effectiveness and Side Effects Compared
Both Rigevidon and Microgynon are over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy when taken correctly. This means fewer than 1 in 100 users will become pregnant each year if the pill is taken as prescribed. However, effectiveness can decrease if pills are missed, vomited, or affected by certain medications.
Common Side Effects
Since both pills contain the same hormones, they share similar side effects, which may include:
- Nausea
- Headaches
- Mood changes
- Breast tenderness
- Breakthrough bleeding (spotting between periods)
These often improve after a few months as the body adjusts.
Potential Risks
Like all combined contraceptive pills, both carry a small risk of blood clots, particularly for smokers, people over 35, or those with certain health conditions. Rare but serious side effects include:
- High blood pressure
- Migraines with aura
- Blood clots in the legs or lungs
If you experience severe leg pain, chest pain, or shortness of breath, seek medical attention immediately.
How to Choose the Right Pill for You
Deciding between Rigevidon and Microgynon depends on personal health, side effects, and past experiences. Although both pills contain the same hormones, individual reactions can vary.
If you’ve used one of these pills before without issues, it may be best to continue with it. However, if you experience unwanted side effects, switching to the other may help, even though the ingredients are identical. Those with certain health conditions, such as migraines with aura or a history of blood clots, may need to consider alternative female contraception, like the mini pill or non-hormonal options.
A doctor or pharmacist can help determine the best choice based on your medical history and previous experiences. If neither pill suits you, other combined pills or long-acting methods like the implant or IUD may be worth exploring. Switching pills is common and can be done with medical guidance.
Rigevidon and Microgynon have nearly identical compositions, but individual responses can vary. Both are effective when taken correctly, though side effects may differ. Finding the right option depends on your medical history and how you tolerate the hormones. If one doesn’t work well for you, switching to another combined pill or a different contraceptive method is possible.
For guidance on the best choice, WePrescribe offers expert support through a video consultation or you can contact us for further assistance.